In this blog entry, we would like to introduce an aspect of link building which too often goes unrecognised but could really help improve your strategy, namely turning broken pages and links into functioning links. As we shall see, this applies both to your own website and – with the help of the webmaster – to external domains. Let’s take a closer look.
What are broken links?
As the name suggests, broken links are links which no longer work when you click on them. They lead to content which no longer exists or which for technical reasons has never existed. Such links usually return a 404 or 410 HTTP status code error from the server. Well optimised pages feature customised 404 pages, whilst other users are simply faced with an error message.
Broken pages – an on-page issue
Websites go through many changes with content often deleted or moved around, or the URL structure being altered. These can lead to pages no longer being accessible or similar pages being merged into one summary page. When other webmasters like your content (which is of course a good thing!), they will link to it from their own pages and blogs. This leads to good, natural link building and keeps Google happy. But when content is moved and this is not signalled by a redirect, users following the link suddenly come up against a 404 error. Not only that, vital link juice is wasted and Google can’t crawl your page as its crawler keeps running into dead ends.
Use the XOVI Link Tool to filter out these broken pages, fix errors and optimise your quality and quantity or your backlinks. As an example, let’s have a look at our ornithological friends over at FunkyPigeon.com. Start by entering the domain in the search bar at the top of the XOVI Suite.
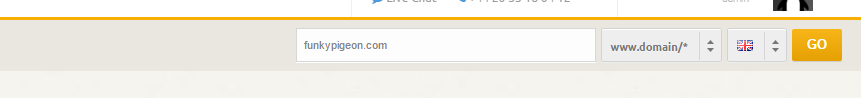
Now use the main menu to access Links > Broken Pages. The table contains a list of pages on the domain which are not accessible. In other words, broken pages.
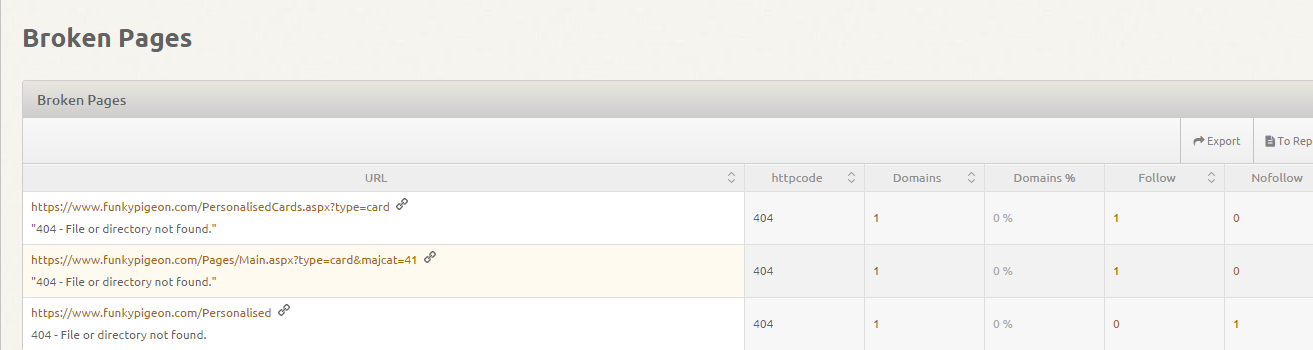
The list doesn’t only have to contain affected HTML pages, but could also feature files such as .jpg or .png images. Click on the plus button on the right hand side to expand each item and see where exactly backlinks to these broken pages come from. These could be highly desirable or valuable backlinks which are currently wasted.
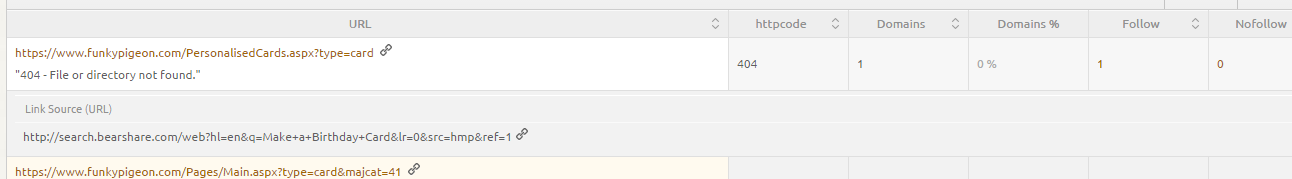
Open up the link target URL (https://www.zalando.co.uk/asdf) to have a look at your broken page. In this case, the user sees an ugly server error message. Many webmasters customise their 404 error pages with humorous or friendly messages and helpful links to allow the user to continue their journey. Nevertheless, an effective redirect is still preferable.
Now, double check the link source URL to decide if a link from this website is worth making “usable” again, or whether it’s better left extinct to protect yourself from the Penguin Update.
If you decide you would like to fix the link, redirect the link to an existing page using a 301 redirect. This should ideally be a page where the original content has been moved to or which features similar content. This allows the link juice to flow again.
Conclusion
It’s relatively easy to identify broken pages which have been lost during the course of structural changes to your domain and to reactivate them to make your page usable again. Instead of having to contact to link source webmaster and ask them to change the link, you can fix the problem yourself with a redirect. The XOVI Suite enables you to quickly identify broken pages and react appropriately.
Broken links – an off-page issue
As with the broken pages above, this method can also be used for external websites. There’s nothing new about this method – SEO buffs and link builders have been using it for a while. But since our XOVI family also includes a large number of SEO newbies, now is an ideal opportunity to take a closer look.
When it comes to broken links, we’re looking for backlinks from thematically relevant websites to our own domain which no longer work or which link to locations which are no longer accessible. In effect, we’re on the hunt for broken links on external pages. This can be done manually by accessing these websites and clicking on external links to double check that they still work. Of course, this is quite time consuming, so this is where XOVI comes into play. This time, we need XOVI’s On-Page Tool.
As always in the On-Page Tool, a project must already have been set up for the domain in question. Only then can an on-page analysis be carried out. We explained how to do this in a recent blog post, which you can access here. Remember: you can set up as many projects as you like in XOVI, so don’t worry about using up any quotas or anything like that! If you don’t need a project any more, simply delete it.
Having set up the project, switch over to analysis management in the On-Page Tool and set up a new on-page analysis.
Once the analysis is complete, access the analysis results and head to “External links > All external links” to view a list of all external links. XOVI gives the status code for each link. With small lists, you can see external links with 404 or 410 HTTP status codes at a glance, whereas with longer lists you might like to apply the relevant filters.
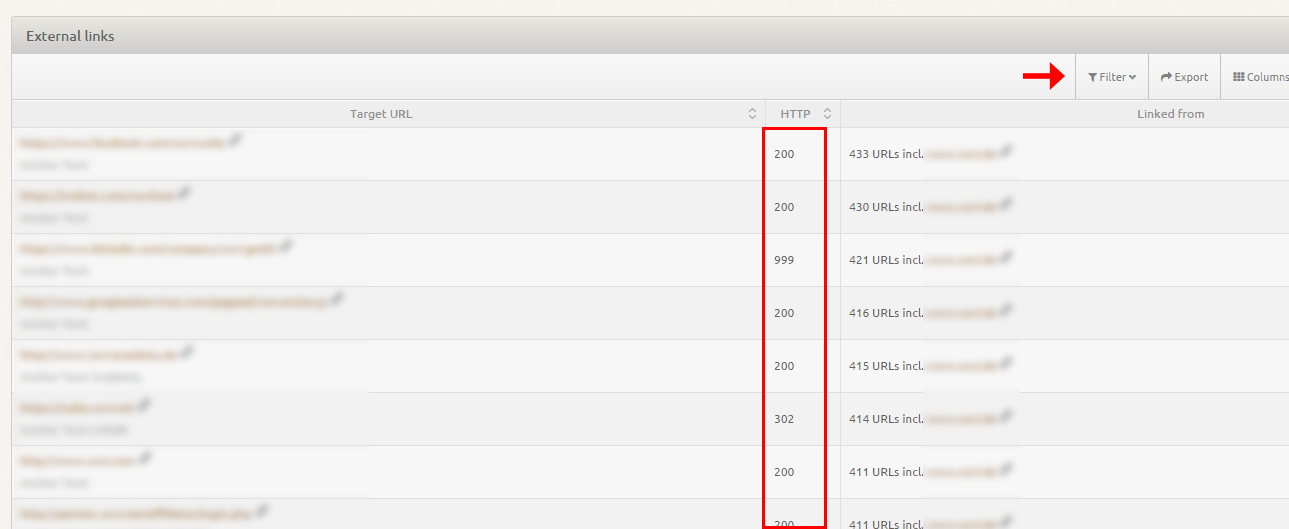
Now what? Contact the external webmasters!
If your website still features content relevant to the original backlink, inform the external webmaster and ask him or her to adjust the “broken” link so that it now points to relevant content.
If you no longer have suitable content relevant to the website providing the backlink, create some! It would be a shame to lose a valuable backlink from a quality site! If you’re stuck for inspiration, have a look at what used to be under the URL in a web archive such as http://archive.org/web. But be careful – don’t just copy! Most texts stored here are copyright protected so any reproduction is simply illegal. But you should certainly have a read through and use the content for inspiration.
Conclusion
There is potential in this second method, too. Indeed, webmasters are generally happy for the heads up. After all, they don’t want broken links on their page either! Just remember to be friendly and professional, and you’ll soon be able to repair the backlink for the benefit of both parties.